A team of researchers led by Professor Young S. Park at UNIST’s Department of Chemistry has achieved a significant breakthrough in the field of organic semiconductors. Their successful synthesis and characterization of a novel molecule called “BNBN anthracene” has opened up new possibilities for the development of advanced electronic devices.
Organic semiconductors play a crucial role in improving the movement and light properties of electrons in carbon-centered organic electronic devices. The team’s research focused on enhancing the chemical diversity of these semiconductors by replacing carbon-carbon (C−C) bonds with isoelectronic boron-nitrogen (B−N) bonds. This substitution allows for precise modulation of the electronic properties without significant structural changes.
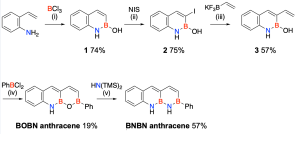
The researchers successfully synthesized the BNBN anthracene derivative, which contains a continuous BNBN unit formed by converting the BOBN unit at the zigzag edge. Compared to conventional anthracene derivatives composed solely of carbon, the BNBN anthracene exhibited significant variations in the C−C bond length and a larger highest occupied molecular orbital–lowest unoccupied molecular orbital energy gap.
In addition to its unique properties, the BNBN anthracene derivative demonstrated promising potential for application in organic electronics. When used as the blue host in an organic light-emitting diode (OLED), the BOBN anthracene exhibited a remarkably low driving voltage of 3.1V, along with higher efficiency in terms of current utilization, energy efficiency, and light emission.
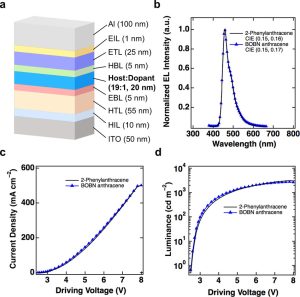
The research team further confirmed the properties of the BNBN anthracene derivative by studying its crystal structure using an X-ray diffractometer. This analysis revealed structural changes, such as bonding length and angle, resulting from the boron-nitrogen (BN) bonding.
“Our study on anthracene, a type of acene widely recognized as an organic semiconductor, has laid the groundwork for future advancements in the field,” commented Songhua Jeong (Combined MS/Ph.D. Program of Chemistry, UNIST), the first author of this study. “The continuous BN bonding synthesized through this research holds great potential for applications in organic semiconductors.”
Professor Park emphasized the significance of this breakthrough, stating, “The synthesis and characterization of compounds with continuous boron-nitrogen (BN) bonds contribute to fundamental research in chemistry. It provides a valuable tool for synthesizing new compounds and controlling their electronic properties.”
The research findings, which also involve the contributions of Professor Joonghan Kim’s team from the Catholic University of Korea, Professor Wonyoung Choe’s team from the Department of Chemistry at UNIST, and a research team from SFC Co., Ltd., were published online on December 11 in the prestigious journal, Angewande Chemie International Edition. The study received support from the mid-sized research enterprise SFC and was promoted by the National Research Foundation (NRF) of the Ministry of Science and ICT, under the projects of the Ministry of Trade, Industry, and Energy.
Journal Reference
Seonghwa Jeong, Eunji Park, Jiyeon Kim, et al., “Increasing Chemical Diversity of B2N2 Anthracene Derivatives by Introducing Continuous Multiple Boron-Nitrogen Units,” Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., (2023).



